Structure of Super Absorbent Polymers
Superabsorbent polymers are non-toxic polymers that can absorb more than a hundred times their weight very quickly and do not release liquid under pressure. These polymers are used in diapers, adult diapers, feminine hygiene products, absorbent medical clothing, agricultural applications and other industrial applications. With its use in diapers, it increases the fluid holding capacity of the diapers and reduces the use of cellulose, making it possible for the diaper to have a thinner structure.
The super-absorbent polymers used in diapers are sodium polyacrylate. This hydrophilic, water-loving polymer has sodium (NA+) and carboxylate (COO-) ions in its structure. When the neutral polymer comes into contact with water or aqueous solutions, these plus and minus charges in its structure interact with water molecules. Because the water molecule (H2o) is a polar molecule because positive charges are concentrated on hydrogen atoms and negative charges are concentrated on the oxygen atom. This increases the strength of the bonds between water molecules and allows water to interact with electrically charged particles.
The Na+ ions that interact with the oxygen atom of the water are dissolved in water and separated from the chain. Since the COO-ions remaining on the polymer chains are the same charge, they begin to repel each other with electrostatic force. Thus, the polymer ball expands. However, thanks to the cross-links that allow the formation of a network between the chains, the polymer is insoluble in water. The expanding polymer ball can take more water into it. Since the COO- ions on the chain interact with the water molecules, the water that enters between the polymer chains is retained by the polymer.
Na ions separated from the polymer chain move freely within the polymer network, but do not leave the polymer network because they are attracted by the COO ̄ in the polymer chain, albeit weakly. Therefore, the ion density in the polymer network is higher than in the medium in which the polymer is located. Due to this density difference, water moves from a less dense medium to a very dense medium and enters between the polymer chains, and the polymer swells.
If salt (NACl) is added to the medium where the polymer is located, the ion concentration of the medium increases. In this case, the water molecules held by the polymer pass into a denser medium, and the negatively charged groups on the polymer chains are neutralized by the sodium ions in the medium. In this way, the polymer chains pass into each other again and become irregular.
How Does Sap’s Swelling Mechanism Work?
The amount of absorption in 0.9% salt water under the free surface conditions of SAP is defined as “swelling capacity”.
Sodium polyacrylate is used as SAP in diapers. The main body of this polymer consists of water-loving carboxylic acid (COO ̄) groups. When water is added to SAP, polymer-solvent interaction occurs, followed by hydration and hydrogen bonds.
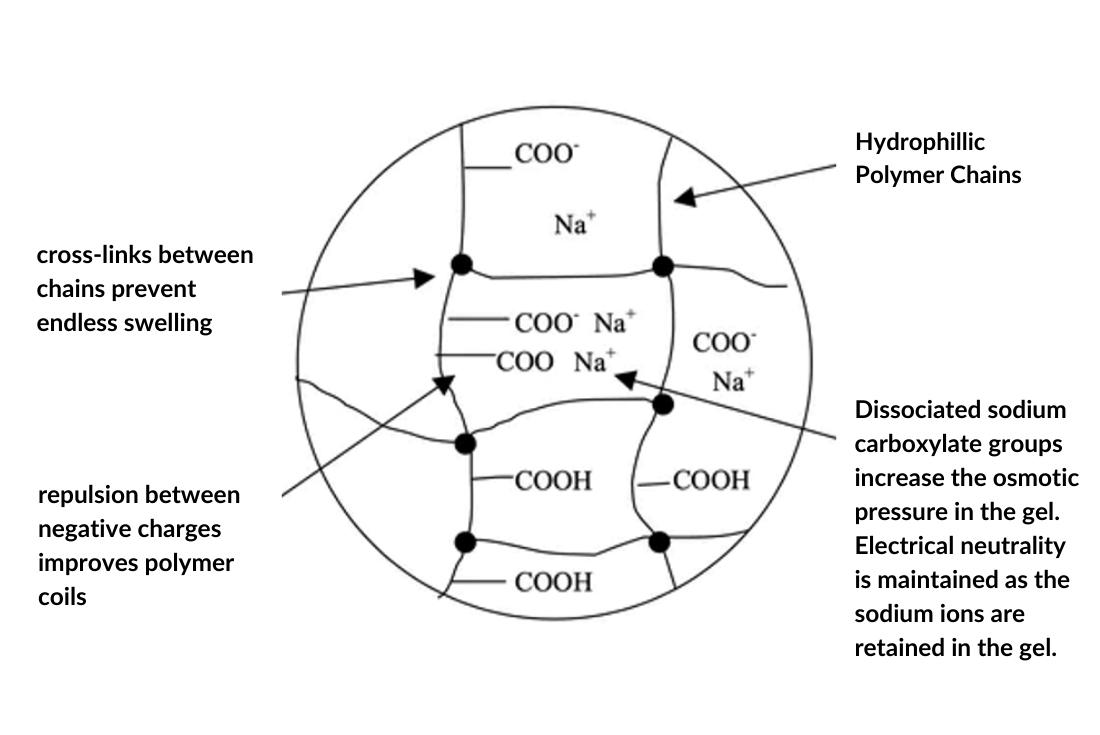
The resulting SAP network is shown below.
1-HYDRATION
Hydration is defined as the interaction between the ions of the solute and the molecules of the solvents.
Sodium polyacrylate polymer has sodium (Na+) and carboxylate (COO ̄) ions. When the neutral polymer comes into contact with water or aqueous solutions, these plus and minus charges in its structure interact with water molecules, turning into a molecule in which the positively charged hydrogen atoms and the minus charged oxygen atom in the water molecule are concentrated. With COO ̄, the attraction of Na+ ions to polar water molecules is shown schematically.

1-1 Hydrogen Bonds
Hydrogen bonds are defined as electrostatic interactions between molecules. It is formed by the bonding of hydrogen atoms in molecules to light electronegative atoms such as N, F, O, and hydrogen atoms affect free electron pairs on neighboring electronegative atoms.
Electronegative oxygen atoms, which attract hydrogen electrons in water, form dipole bonds within the molecule; positively charged hydrogen atoms attract free oxygen pairs in other water molecules. The hydrogen bonds formed within the water molecule are seen schematically below:

1-2 Swelling of SAPs without Dissolving in Water
The Na+ ions that interact with the oxygen atom of the water are dissolved in water and separated in the chain, and the COO- ions remaining on the polymer chains begin to repel each other with electrostatic force because they are the same charged. Thus, the polymer ball expands, but the polymer does not dissolve in water thanks to the cross-links that provide network formation between the chains. The expanding polymer ball is able to take more water into it, and the water between the polymer chains is trapped and trapped by the polymer as the COO-ions on the chain interact with the water molecules.

1-3 Osmotic Pressure and Swelling in Ionic Fluid
The swelling of the superabsorbent polymer in the ionic liquid occurs differently. Although the Na+ ions separated from the polymer chain are weak in moving freely within the polymer network, they cannot leave the polymer network because they are attracted by COO- in the polymer chain. Therefore, the ion density in the polymer network is higher than the density in the medium where the polymer is located, and depending on this density difference, the water moves from the less dense medium to the very dense medium and enters between the polymer chains, thus swelling the polymer.
1-4 The Effect of Cruciate Ligaments and Neutralization on Swelling
As the density of the cruciate ligament decreases, the swelling capacity of the polymer increases. The increase in the degree of neutralization (Dn) also increases the swelling capacity.

2-CROSS-LINKING IN SAPS
In the production of super-absorbent polymers, cross-linking is carried out in two ways: mass cross-linking and surface cross-linking.
2-1 Mass Cross-Linking
Cross-linking is applied to bind two or more macromolecules together and is done at the polymerization stage.
Covalent cruciate ligament is widely used in SAP production . Cross-links are organic molecules containing two or more polymerizable double bonds. These molecules are incorporated into the backbone of the polymer chain and grow during the polymerization reaction.

2-2 Surface Cross-Linking
SAP’s swelling rate and fluid retention under pressure are improved by applying cross-linking to the outer surface of the particles. Surface cross-linkers are applied as a finishing treatment on dried, ground and dimensioned SAP particles. The particles are treated with a solution that acts as a cross-linker and subjected to heat treatment. As a result of this process, the density of cross-linkers on the outer surface of the particle increases and can be called center-shell. Low density cross-linking is seen in the center of the particle, while high density cross-linking is seen in the crust region on its surface.

Cross-linking to the surface of the SAP part i ashes is very important in giving the product the desired properties. A polymer of good quality can be given different performance characteristics with different coating solution and cross-linker.

REFERENCES
- Akar,E ‘’Aktif Polimerlerin Hazırlanması ve Karakterizasyonu’’ Yüksek lisans Tesi,Dokuz Eylül Üniversitesi Fen Bilimleri Enstitüsü Kimya Anabilim Dalı,İzmir, (2012)
- Esra O , ‘’ Bebek Bezlerinin Performansını Etkileyen Özelliklerin Araştırılması ve Performans Özelliklerinin Karşılaştırılması ‘’ Pamukkale Üniversitesi Fen bilimleri Enstitüsü Tekstil Mühendisliği Anabilim Dalı Yüksek Lisans Tezi, (2018)
- Bilgici,Z, ‘’Bebek Bezindeki Polimerler Sıvıyı Nasıl Emer? ‘’ (16.12.2016) http://bilimgenc.tubitak.gov.tr/makale/bebek-bezindeki-polimerler-siviyi-nasil-emer,2016
- Bartkowiak,G, Frydrych, I , ‘’ Superabsorbents and their madical applications’’ , Bartels, V.T. (Ed), Handbook of Medical Textiles,Cambridge:Woodhead Publishing Limited, 505-546, (2011)
- Bulleri, B, ‘’ The Vortex Effect: liquid holding properties for fluffless and thinner diapers’’ , Insight 2014 Conference, Indianaoplis, (2014)
- Lee, S , ‘’Super Absorbent Polymer Market:Market Size and Market Trends Till 2020 ‘’, (2016) https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/super-polymer-market-size-trends-till-2020-smith-lee, (2015)
- Satellite Science and Tecnology Co., Ltd, 2018
- edana.org




Leave A Comment